Medical Disclaimer
This article is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed healthcare professional before starting, adjusting, or stopping any medication, including semaglutide or Rybelsus.
Author: Dr. David R. Dansie, Family Medicine Physician.
Semaglutide’s Expanding Role in U.S. Healthcare
By 2025, semaglutide has become one of the most influential GLP-1 receptor agonists used in American healthcare. Increased awareness, strong clinical outcomes, and reliable safety data have positioned it as a cornerstone of modern metabolic therapy. Patients researching what is semaglutide often do so because they’ve heard about its success not only in controlling blood sugar but also in supporting healthier eating habits, reducing cravings, and helping manage long-term metabolic conditions. Clinicians across the country report that semaglutide discussions now occur daily in primary care, endocrinology, and obesity-medicine practices, reflecting its widespread impact.
Safe Access Through Licensed Pharmacies
Semaglutide should always be obtained through legitimate medical providers and FDA-regulated pharmacies. This greatly reduces the risks associated with counterfeit or improperly compounded products circulating online. Patients looking for safe dispensing options can rely on trusted, community-based locations such as: Sweetwater Medical Center Pharmacy
Licensed pharmacies ensure medication authenticity, correct formulation, and proper storage all essential components of safe GLP-1 therapy. This is especially important as consumer demand grows and more individuals seek semaglutide-based treatment options across the United States.
Why Semaglutide Became a Leading GLP-1 Treatment
Several factors contribute to semaglutide’s popularity in 2025:
- extensive clinical validation from multiple randomized trials
- long-term data confirming sustained therapeutic effects
- availability in both injectable and oral semaglutide formulations
- its broad benefits on appetite regulation, glucose control, and metabolic health
The arrival of Rybelsus, the first and only oral semaglutide tablet, was a major milestone. Many patients hesitant about injections now have a clinically supported alternative. This flexibility allows clinicians to tailor treatment to a patient’s preferences, lifestyle, and comfort level a key principle in today’s personalized medical care. Understanding how semaglutide works gives patients a foundation for making informed decisions, which leads directly into the next section.
How Does Semaglutide Work? Understanding the GLP-1 Mechanism
The question how does semaglutide work remains one of the most commonly asked among new patients. The medication’s effectiveness stems from its ability to mimic GLP-1 a natural hormone responsible for regulating appetite, digestion, and blood sugar. Because GLP-1 levels can be impaired in people with metabolic disorders, semaglutide functions as a targeted replacement that restores healthier metabolic signaling.
GLP-1 Receptor Activation: A Deeper Look at the Biology
Once semaglutide binds to GLP-1 receptors, it activates several interconnected pathways:
- Enhanced insulin secretion, but only when glucose levels are high
- Reduced glucagon, preventing excess sugar release from the liver
- Slower gastric emptying, which moderates post-meal glucose spikes
- Improved satiety, helping reduce overeating and late-night cravings
These mechanisms work simultaneously, which is why patients often report benefits across multiple metabolic areas. Unlike older diabetes medications that targeted only one pathway, semaglutide’s multi-system engagement contributes to more stable outcomes.
Therapeutic Versatility: Why Semaglutide Helps Different Populations
The GLP-1 mechanism benefits both people with diabetes and individuals seeking metabolic health improvements. Patients often describe fewer cravings, better control over portion sizes, and more predictable energy patterns. Clinicians appreciate the predictable pharmacologic effect, consistent research outcomes, and relatively low risk of hypoglycemia. This versatility explains why semaglutide has become a preferred option for improving metabolic health across diverse patient groups.
Injectable vs. Oral Semaglutide: Technological Breakthrough
For years, GLP-1 medications were available only as injections because the digestive tract destroyed peptide-based drugs. The development of oral semaglutide featured in Rybelsus required an advanced absorption enhancer that protects semaglutide through the stomach and allows it to enter the bloodstream. This innovation dramatically broadened patient access by offering a non-injectable alternative that still provides clinically meaningful results.
Clinical Research Supporting the Mechanism
Between 2021 and 2025, journals such as NEJM, JAMA, and Diabetes Care published numerous studies confirming the reliability of semaglutide’s metabolic effects. Research continues to show improvements in glycemic control, appetite regulation, and long-term metabolic health. This strong evidence base is one of the main reasons clinicians feel confident recommending semaglutide as part of a patient’s individualized treatment plan.
Forms of Semaglutide in 2025: Injections, Oral Options, and the Role of Rybelsus
Semaglutide is available in several FDA-approved formulations, giving clinicians flexibility when designing treatment plans. In 2025, patients can choose between weekly injectables and a daily oral medication, each supporting different lifestyle needs. These options are not interchangeable, and understanding the differences helps patients feel more confident when discussing treatment choices with their physician. As semaglutide’s popularity continues to grow, clear guidance on forms and delivery methods has become essential.
Injectable Semaglutide: Weekly Treatment With High Consistency
Injectable semaglutide remains the most widely used form in clinical practice. It is administered once per week using a small, pre-filled injection device designed for at-home use. One of the key strengths of injectable formulations is their highly consistent absorption profile because they bypass the digestive system, the body receives the medication in a predictable way. This reliability makes weekly injections a strong fit for patients who value simplified routines, travel frequently, or struggle with daily medication schedules.
In addition, injectables have been the subject of numerous large-scale clinical studies, giving physicians a deep, long-term evidence base to draw from. For many adults managing type 2 diabetes or metabolic health concerns, the weekly format fits seamlessly into their lifestyle with minimal daily disruption.
Oral Semaglutide and Rybelsus: A Pill That Changed the GLP-1 Landscape
Rybelsus introduced an entirely new option: a tablet form of semaglutide. This innovation required advanced absorption technology, allowing the medication to survive stomach acid and enter the bloodstream something previously impossible for GLP-1 drugs.
For patients who feel uneasy about injections or prefer a familiar pill format, Rybelsus offers a meaningful alternative. It appeals particularly to individuals who already take multiple oral medications or who associate daily pills with routine and structure. However, oral administration also requires greater consistency: it must be taken on an empty stomach with water, and patients must wait before eating.
This format is not “better” or “worse” than injectables instead, it reflects how diverse patient needs have become. Many appreciate its simplicity and needle-free delivery, while others prefer the convenience of once-weekly dosing.
Upcoming Innovations: What Patients Can Expect in the Next Two Years
The rapid advancement of GLP-1 therapies shows no signs of slowing. Between 2025 and 2027, researchers expect several new developments:
- Enhanced oral GLP-1 formulations that improve absorption
- Combination drugs targeting multiple metabolic pathways (e.g., GLP-1/GIP)
- New delivery systems designed to reduce side effects
- Longer-acting oral medications requiring fewer doses
These future treatments reflect a major shift in modern metabolic medicine: patients want therapies that are safe, effective, and easy to use long-term. The development of these medications signals a move toward a more personalized, patient-centered approach in managing both diabetes and metabolic disorders.
FDA-Approved vs. Compounded Semaglutide: Why Knowing the Difference Matters
Not all semaglutide available on the market is the same. As demand has grown, so has the number of unregulated or unauthorized products especially online. The distinction between FDA-approved medications and compounded versions is critical for safety, legality, and treatment success. Understanding these differences allows patients to make informed decisions and avoid potential harm.
Compounded Semaglutide: A Growing Trend With Significant Risks
Compounded semaglutide has gained visibility due to its lower price and aggressive marketing, but it comes with notable concerns. This format is prepared in compounding pharmacies rather than FDA-regulated manufacturing facilities. Some compounded products use chemicals that are not identical to semaglutide for example, semaglutide sodium or acetate which differ from the FDA-approved ingredient.
Because compounded versions are not subject to the same quality controls, patients may face risks related to contamination, incorrect dosing, reduced potency, or unexpected side effects. While compounding plays an important role in medicine, it becomes dangerous when used to recreate complex drugs that require strict production standards.
Why FDA Approval Ensures Higher Safety and Quality
FDA-approved semaglutide goes through extensive testing for purity, potency, sterility, and safety. These products are manufactured in highly controlled environments and continuously monitored for adverse events. This level of oversight protects patients from harmful variations and ensures that every dose meets strict medical standards.
When clinicians recommend semaglutide, they rely on clinical validation from large trials. Compounded versions rarely undergo this type of testing, meaning patients may not receive the same therapeutic results and in some cases may be exposed to harmful impurities.
Buying Semaglutide Online: How to Identify Safe Sources
With more people seeking treatment online, the risk of encountering fraudulent or unsafe sources has increased. Websites offering “no prescription required,” unusually low prices, or unclear pharmacy credentials should be avoided. These sellers often distribute counterfeit products or unregulated compounded formulations.
Safe online access always requires:
- a valid prescription
- a licensed U.S. pharmacy
- transparent contact information
- clear storage and dispensing standards
Semaglutide Dosing Explained: How Clinicians Adjust Treatment for Safety and Effectiveness
Semaglutide dosing plays a major role in achieving safe and predictable results, and physicians carefully customize dosing plans based on the patient’s metabolic profile, treatment goals, and tolerance. Because semaglutide activates GLP-1 receptors that influence insulin secretion, appetite regulation, and digestive speed, proper titration helps reduce early discomfort and improves long-term adherence. The gradual dose-increase strategy is one reason why patients frequently search for clear guidance on semaglutide dosing, wanting to understand how the medication is typically adjusted over time.
Clinicians typically begin with a low introductory dose designed to help the body adapt before moving to therapeutic levels. This approach minimizes early gastrointestinal symptoms while allowing the patient to experience progressive benefits. Higher doses are often considered once the patient shows good tolerance and requires a stronger metabolic effect. It is important to emphasize that dosing is never a one-size-fits-all process each adjustment depends on personal health factors and ongoing medical evaluation.
Example Semaglutide Dose Progression
| Stage | Typical Dose (Example) | Purpose | Notes |
| Initiation | Low starting dose | Allows the body to adapt | Reduces early GI discomfort |
| Therapeutic | Mid-range dose | Provides intended metabolic effect | Evaluated after several weeks |
| Advanced | Higher dose option | Stronger appetite & glucose response | Not suitable for every patient |
This table is for educational purposes only. Actual dosing decisions must be determined by a licensed healthcare professional.
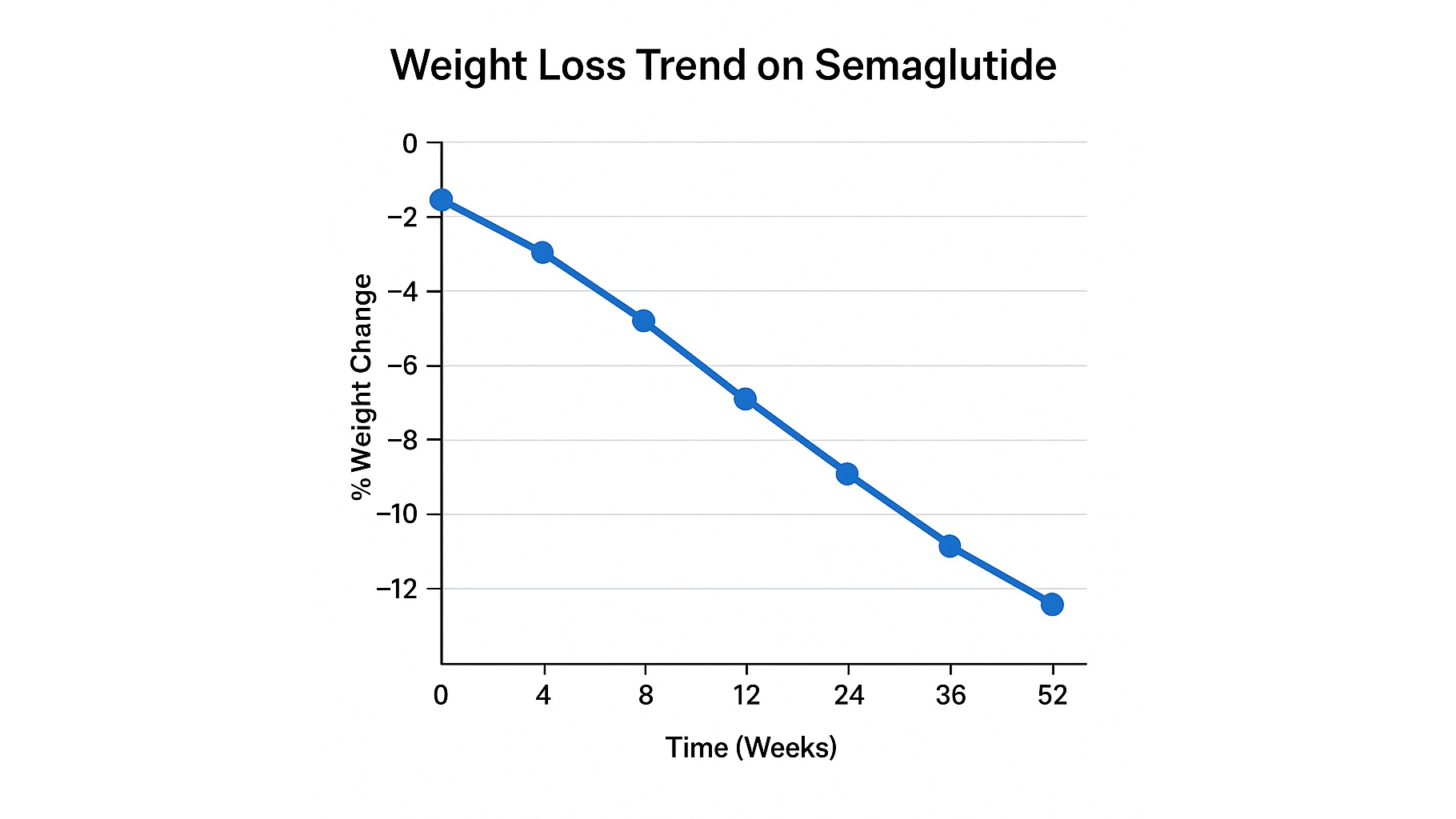
Semaglutide for Weight Loss: What Research Shows About Effectiveness in 2025
Semaglutide has significantly changed how clinicians approach medical weight management. Clinical studies conducted between 2021 and 2025 consistently demonstrate that semaglutide supports meaningful reductions in appetite, caloric intake, and overall body weight. Because these findings have been replicated across diverse patient groups, the medication has become a major point of interest for adults seeking structured metabolic support making semaglutide for weight loss one of the most frequently searched topics in the country.
What makes semaglutide unique is its ability to influence multiple pathways involved in hunger and fullness. Patients often report reduced cravings, fewer late-night eating episodes, and improved control over portion sizes. While results vary, many clinical trials report a steady and predictable pattern of weight reduction over time, especially when combined with healthier eating habits and consistent follow-up with a physician.
To explore semaglutide’s use in obesity via the oral form Rybelsus, check Rybelsus for Weight Loss – How Oral Semaglutide Is Changing Obesity Treatment.
These effects do not occur overnight. Weight changes typically develop gradually over weeks and months, aligning with how GLP-1 pathways regulate appetite and digestion. Physicians emphasize patience and consistency and always remind patients that semaglutide is a tool within a broader health strategy, not a standalone solution.
Semaglutide Side Effects and Safety Profile: What Patients Report in 2025
Semaglutide is one of the most deeply researched GLP-1 therapies available in 2025, and its safety profile is supported by large-scale clinical trials, long-term observational studies, and FDA post-marketing data. Patients frequently ask about semaglutide side effects, especially when beginning treatment or increasing their dose. Understanding the typical experiences and how to prepare for them can significantly improve comfort and confidence during therapy.
Most Common Short-Term Experiences
Gastrointestinal symptoms are the effects most patients notice during the early phase of therapy. These may include reduced appetite, nausea, increased fullness, or changes in digestion. Such responses are not unexpected; they reflect how GLP-1 receptor agonists regulate appetite signals and slow gastric emptying. In most cases, symptoms gradually improve as the body adapts.
Less Common Effects Observed in Clinical Studies
Although far less frequent, some individuals may report fatigue, mild abdominal discomfort, or changes in taste. Larger clinical trials continue to show that side effects of semaglutide generally remain manageable when dosing is increased gradually under supervision.
How Long Do Side Effects Last?
A question patients frequently ask is: how long do semaglutide side effects last?
While the experience varies from person to person, many patients find that the most noticeable symptoms occur during the first 2–6 weeks of each dose level. As dosing stabilizes, the frequency and intensity typically decline. Your physician may adjust the pace of dose increases to improve tolerability.
Is Semaglutide Safe?
Patients also commonly ask whether semaglutide is safe in the long term. Clinical evidence through 2025 shows a strong safety profile, with consistent results across multiple populations. Still, is semaglutide safe for every individual? Not necessarily people with certain medical conditions or taking specific medications may require careful monitoring. This is why individualized care and ongoing communication with a healthcare professional remain essential.
Oral vs Injectable Semaglutide: Effectiveness, Convenience, and Patient Preference
With options available in both oral and injectable forms, semaglutide offers flexibility unmatched by many other metabolic therapies. Some adults appreciate the convenience of weekly injections, while others prefer the familiarity of a daily tablet such as Rybelsus. Comparing the two can help patients understand which method may better fit their lifestyle, preferences, and long-term health goals.
For a head-to-head comparison of injectable vs oral semaglutide, visit Ozempic vs Rybelsus (2025) – Which Is Better for Diabetes & Weight Loss?
Oral Semaglutide (Rybelsus) vs. Injectable Semaglutide(Ozempic)
| Feature | Oral Semaglutide (Rybelsus) | Injectable Semaglutide |
| Dosing Frequency | Taken daily | Once weekly |
| Ease of Use | No needles | Minimal daily routine |
| Absorption | Variable, affected by timing | Stable and predictable |
| Lifestyle Fit | Good for patients who prefer pills | Good for patients who want less frequent dosing |
| Clinical Evidence | Growing body of research | Extensive long-term data |
Where Semaglutide Fits Into Modern Metabolic Health (2025 Clinical Perspective)
Semaglutide has become a central part of metabolic-health management in 2025, supporting patients with type 2 diabetes, obesity, or long-standing difficulty regulating appetite and blood sugar. Clinicians now commonly combine semaglutide therapy with broader lifestyle strategies including nutrition, movement, sleep quality, and stress management to improve long-term outcomes.
For the oral semaglutide option in diabetes, see Rybelsus for Type 2 Diabetes Treatment: Updated Overview for 2025.
From a family medicine perspective, semaglutide represents an important shift in chronic-disease care:
- It supports sustainable behavior change
- It reduces the burden of traditional glucose-lowering medications
- It provides benefits across metabolic pathways, not just blood sugar
As research expands and newer GLP-1 and GIP-based therapies emerge, semaglutide remains one of the most thoroughly validated and widely trusted treatment options available.
FAQ: Most Common Questions About Semaglutide
What is semaglutide used for in 2025?
It is used to support metabolic health, help regulate appetite, and assist adults with type 2 diabetes or weight-related conditions under medical supervision.
How does semaglutide work in the body?
It mimics the GLP-1 hormone, which supports insulin secretion, reduces appetite, slows digestion, and helps stabilize blood sugar.
Is semaglutide safe for long-term use?
Large studies through 2025 show strong long-term safety, but individual factors vary. A licensed clinician must assess risks and suitability.
Should I be concerned about compounded semaglutide?
Compounded versions may differ in purity, quality, and formulation. FDA-approved semaglutide is considered the safer and more reliable option.
How long do semaglutide side effects last on average?
Most early symptoms improve after the first few weeks of treatment or after stabilizing at a new dose.
Can semaglutide help with weight loss?
Many adults experience reduced appetite and gradual weight reduction, particularly when the medication is paired with lifestyle changes.
Resources
FDA – Semaglutide (Ozempic/Wegovy/Rybelsus) Prescribing Information
NIH / NCBI – Semaglutide: Mechanisms, Clinical Evidence, and Safety Review
New England Journal of Medicine – Semaglutide for Weight Management (STEP Trials)
American Diabetes Association – Standards of Care Including GLP-1 and Semaglutide
